Attributes
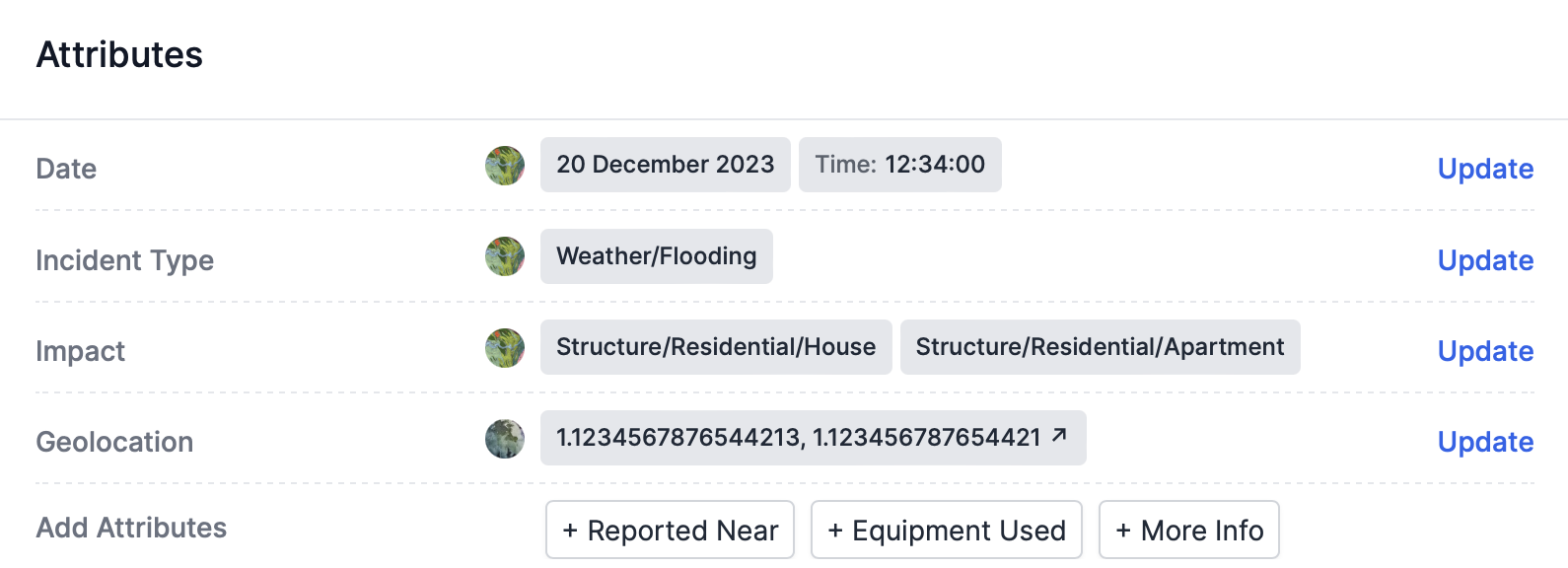
The attribute pane of an incident.
Attributes describe incidents
Attributes are structured data that describe incidents. Attributes make data easily searchable and provide structure for large-scale tagging or data coding projects. Each attribute corresponds to a single column in a spreadsheet-style investigation.
Edit attributes
To add an attribute that doesn’t yet have a value, click on the attribute’s name in the Add Attributes section of the Attributes pane.
To update an attribute that already has a value, click Update on the right side of the Attributes pane.
After opening the Update window:
- Add or edit the attribute’s value(s).
- Optionally explain your change in the provided field. We recommend including an explanation for all non-trivial updates.
- Click Post update. You’ll see the update reflected in the Attributes pane and in the Feed.
Core attributes are permanent
Attributes can be customized for each project, but Atlos provides some basic attributes to help investigators get started. Some of these attributes—like Description, Date, Geolocation, and More Info—are core attributes and can’t be removed from a project’s data model.
Custom attributes
Sometimes the default attributes aren’t sufficient. A project might need attributes or values that better describe its incidents or add more detailed context.
Components of custom attributes
Custom attributes have four components:
Attribute Name— The attribute’s name. Incident Type, for example.
Attribute Type— This refers to the type of data the attribute will contain:
- Text— Text attributes are free-response text boxes. These can be used for one-word values or for longer content.
- Single select— Use single select attributes for selecting a single option from a list of possible values. Use single-select attributes when values are mutually exlcusive.
- Multiple select— Use multiple select attributes for cases when you might need to select multiple options at the same time. For example, the default “Impact” attribute is a multi-select attribute; an airstrike can impact many different kinds of buildings simultaneously.
- Date— The date attribute uses a special date attribute type (displayed as DD Month YYYY, or 08 August 2023). To avoid confusion, there can be only one attribute with the date type per incident.
- Geolocation— The Geolocation attribute uses a special location attribute type. There can be only one attribute with the geolocation type attribute per incident. The Geolocation attribute includes two components. The first is a coordinate pair displayed as latitude, longitude. The Geolocation attribute includes a second component which indicates the precision of the location. There are three possible precision values:
- Exact indicates maximum precision, or ± 10m.
- Vicinity indicates that the indicated location refers to the same complex, block, or field as the true location, or ± 100m.
- Locality indicates that the indicated location refers to the same neighborhood or village as the true location, or ± 1km.
Attribute Description— An optional description of the attribute. We highly recommend including a detailed description of how you expect investigators to use the attribute to avoid confusion.
Attribute Options— Attribute options are the potential values for each attribute. Specify each option by typing a value, pressing Enter, and repeating until you’ve listed every option.
Customize attributes
To customize a project’s data model:
Navigate to the Projects page.
Select the relevant project.
Click on the Manage page and scroll down to the Attributes pane.
a) To add a new attribute to a project’s data model, click Add Attribute on the right side of the Attributes pane.
b) To edit an existing attribute, click the pencil icon to the right of the attribute’s name.
Add or edit the attribute’s Name, Type, Description, or Options.
Click Save.
If you remove an attribute from your project’s data model, that attribute—and its values—will be removed from all incidents in the project.